Demand is the amount of a good or service buyers are willing to purchase at a given price over a defined time period.
Demand for a product reflects the buyer’s perspective. It represents the quantity of a good or service people are willing to purchase at various prices. Generally, as the price of an item increases, people tend to buy less of it. This relationship is explained by the law of demand, which states that—other things being equal—as the price of a good rises, the quantity demanded decreases.
For instance, imagine winter in Madison, Wisconsin, where temperatures often stay well below freezing for days on end. How might this affect the demand for a winter trip to a tropical destination like Hawaii? Naturally, many people would desire such a trip if the price were very low. However, at much higher prices, most would choose to stay home or opt for a more affordable vacation.
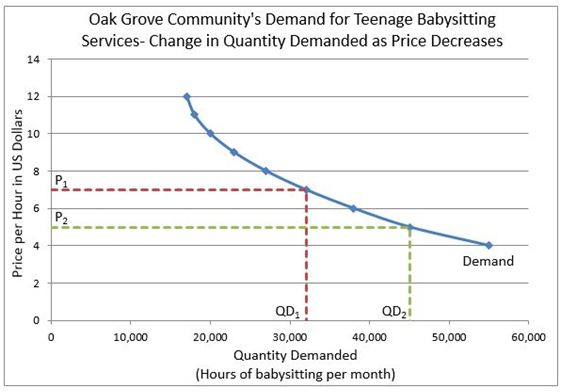
Changes in the price of a good or service lead to changes in the quantity demanded, which are represented by movement along the demand curve. For example, consider the demand curve for babysitting in the Oak Grove community. At a rate of $7.00 per hour, residents demand 32,000 hours of babysitting per month. However, if the rate drops to $5.00 per hour, the quantity demanded increases to 45,000 hours.
Each of us has a demand for every good or service, which may be zero if we would not purchase it at any price. The total of all individual demands constitutes the market demand. Many factors influence individual demand, including income, the prices of related goods (such as substitutes and complements), future expectations, and personal tastes. Companies often use advertising to increase demand for their products. Additionally, the number of potential buyers significantly impacts market demand.
The demand and supply of a good or service together determine its market price and the quantity produced.
Demand – The Consumer's Perspective
Supply and Demand –
Producers and Consumers Reach Agreement
Changes in Demand –
When Consumer Tastes Change
Price Elasticity of Demand –
How Consumers Respond to Price Changes
Supply and Demand –
The Costs and Benefits of Price Controls
Managing Supply Using Tariffs, Subsidies, Quotas & Licenses
Understand a Stock’s Performance Using Supply and Demand